1 X 1 0 X
couponhaat
Sep 19, 2025 · 7 min read
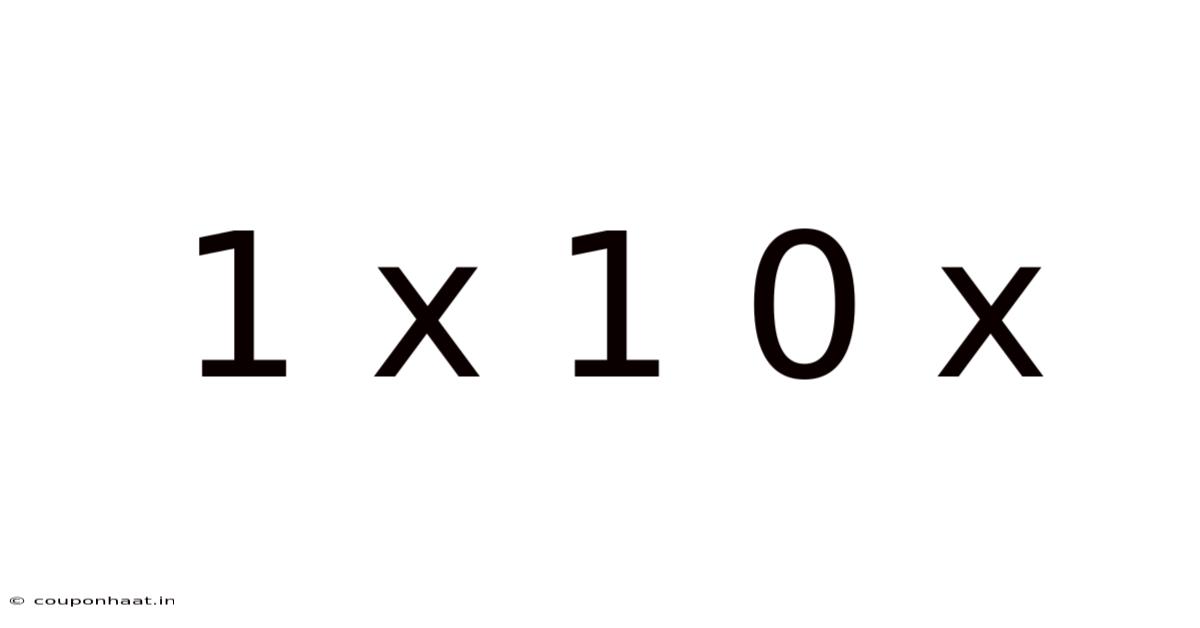
Table of Contents
Decoding 1 x 1 = 0: Exploring Boolean Algebra and its Applications
Understanding the equation "1 x 1 = 0" requires stepping outside the realm of traditional arithmetic and delving into the fascinating world of Boolean algebra. This seemingly paradoxical statement is not a mathematical error, but rather a fundamental principle in a system of logic where numbers represent true (1) and false (0) states. This article will explore the concepts behind Boolean algebra, explain the context of 1 x 1 = 0, and delve into its widespread applications in various fields.
Introduction to Boolean Algebra
Developed by George Boole in the 19th century, Boolean algebra is a type of algebra dealing with logical operations. Unlike traditional algebra that uses numbers and their arithmetic operations, Boolean algebra uses binary variables (0 and 1, representing false and true respectively) and logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT. These operators perform operations on these binary values, resulting in either a 0 or a 1 output.
-
AND Operator: The AND operator (represented by a dot "⋅" or simply juxtaposition) returns 1 only if both inputs are 1. Otherwise, it returns 0. For example, 1 ⋅ 1 = 1, but 1 ⋅ 0 = 0, 0 ⋅ 1 = 0, and 0 ⋅ 0 = 0.
-
OR Operator: The OR operator (represented by a plus sign "+") returns 1 if at least one of the inputs is 1. It returns 0 only if both inputs are 0. For example, 1 + 1 = 1, 1 + 0 = 1, 0 + 1 = 1, and 0 + 0 = 0.
-
NOT Operator: The NOT operator (represented by a bar over the variable or the prime symbol ') inverts the input. If the input is 1, the output is 0, and vice versa. For example, NOT 1 (or 1') = 0, and NOT 0 (or 0') = 1.
Understanding 1 x 1 = 0 in the Context of Boolean Algebra
Now, let's revisit the equation "1 x 1 = 0". In standard arithmetic, this is incorrect. However, within Boolean algebra, this equation can hold true under specific circumstances, primarily involving the modulo-2 arithmetic or the XOR (Exclusive OR) operation.
-
Modulo-2 Arithmetic: Modulo-2 arithmetic is a system where the result of any arithmetic operation is the remainder after division by 2. In this system, 1 + 1 = 0 because 2 divided by 2 leaves a remainder of 0. Similarly, if we consider multiplication in modulo-2 arithmetic, 1 x 1 = 1, but this isn't directly analogous to the statement in question.
-
XOR (Exclusive OR): The XOR operation is a bitwise operator that returns 1 if the inputs are different and 0 if they are the same. It's represented by the symbol ⊕. So, 1 ⊕ 1 = 0 because the inputs are the same, and 1 ⊕ 0 = 1 because the inputs are different. This closely resembles the statement, but the notation is distinct.
Therefore, the statement "1 x 1 = 0" is not a standard Boolean algebra equation using AND, OR, or NOT operators. To accurately represent a scenario where multiplying 1 and 1 results in 0, one must specifically mention either modulo-2 arithmetic or the XOR operator.
Applications of Boolean Algebra
Boolean algebra's power lies in its ability to model logical relationships and control systems. Its applications are vast and impactful across multiple disciplines:
-
Digital Circuit Design: This is arguably the most significant application. Boolean algebra forms the foundation of digital circuit design, allowing engineers to design and analyze logic gates (AND, OR, NOT, XOR, NAND, NOR, etc.) that are the building blocks of all digital electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and embedded systems. Every digital signal is represented as either 0 or 1, and Boolean operations dictate how these signals interact within circuits.
-
Computer Science: Boolean logic is crucial in programming, database management, and algorithm design. Conditional statements (if-then-else), logical operators (AND, OR, NOT), and bitwise operations all stem from Boolean algebra. Data structures like Boolean arrays and flags use Boolean values to represent states.
-
Set Theory: Boolean algebra finds direct correspondence in set theory, where sets can be represented as binary values (membership or non-membership). Operations like union, intersection, and complement directly map to OR, AND, and NOT operations, respectively.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Boolean logic is foundational to many AI and machine learning algorithms. Decision trees, rule-based systems, and some neural network architectures utilize Boolean operations to process information and make decisions.
-
Formal Verification: Boolean algebra is extensively used in formal verification techniques to mathematically prove the correctness of hardware and software systems. Model checking and theorem proving rely heavily on Boolean logic.
Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates
Let's look at how Boolean operations manifest physically in digital circuits through logic gates:
-
AND Gate: An AND gate takes two inputs and outputs 1 only if both inputs are 1. Otherwise, it outputs 0.
-
OR Gate: An OR gate takes two inputs and outputs 1 if at least one input is 1. It outputs 0 only if both inputs are 0.
-
NOT Gate (Inverter): A NOT gate takes one input and inverts it. If the input is 1, the output is 0, and vice versa.
-
XOR Gate: An XOR gate outputs 1 if the inputs are different and 0 if they are the same.
These logic gates, built from transistors and other electronic components, are combined to create complex digital circuits that perform arithmetic, logical, and control operations. The design and analysis of these circuits fundamentally rely on the principles of Boolean algebra.
Beyond the Basics: Karnaugh Maps and Boolean Simplification
Designing efficient digital circuits often involves simplifying complex Boolean expressions. Techniques like Karnaugh maps (K-maps) help to minimize the number of logic gates needed to implement a given Boolean function, resulting in smaller, faster, and more power-efficient circuits. K-maps provide a visual way to group together terms in a Boolean expression and simplify it using Boolean algebra theorems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is 1 x 1 = 0 a valid equation in standard mathematics?
A1: No, in standard arithmetic, 1 multiplied by 1 equals 1. The equation 1 x 1 = 0 only holds true within specific systems like modulo-2 arithmetic or when using the XOR operator in Boolean algebra, not in standard mathematical operations.
Q2: What are the practical implications of Boolean algebra?
A2: Boolean algebra has immensely practical implications, especially in computer science and engineering. It forms the basis of digital circuit design, allowing the construction of computers and other digital devices. It's also crucial in programming, database management, and artificial intelligence.
Q3: How is Boolean algebra different from traditional algebra?
A3: Traditional algebra deals with numbers and their arithmetic operations, while Boolean algebra deals with binary variables (0 and 1, representing false and true) and logical operations (AND, OR, NOT). The fundamental operations and their properties differ significantly.
Q4: Can Boolean algebra be used to solve problems outside of computer science and engineering?
A4: Yes, the principles of Boolean algebra can be applied to various fields. Set theory, logic puzzles, and even some aspects of artificial intelligence leverage the concepts of Boolean logic.
Conclusion
While "1 x 1 = 0" might appear counterintuitive at first glance, understanding its context within Boolean algebra reveals its significance. This seemingly simple equation highlights the fundamental difference between traditional arithmetic and the logic-based operations of Boolean algebra. The applications of Boolean algebra are vast and foundational to the digital world we live in, influencing everything from the design of our computers and smartphones to the algorithms powering artificial intelligence. By understanding its core principles, we gain a deeper appreciation for the power and elegance of this remarkable system of logic. Further exploration into Boolean simplification techniques, circuit design, and advanced logic concepts will enhance your understanding and open up a world of possibilities within the realm of digital technology and beyond.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 X 1 0 X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.