2 000 Divided By 12
couponhaat
Sep 14, 2025 · 6 min read
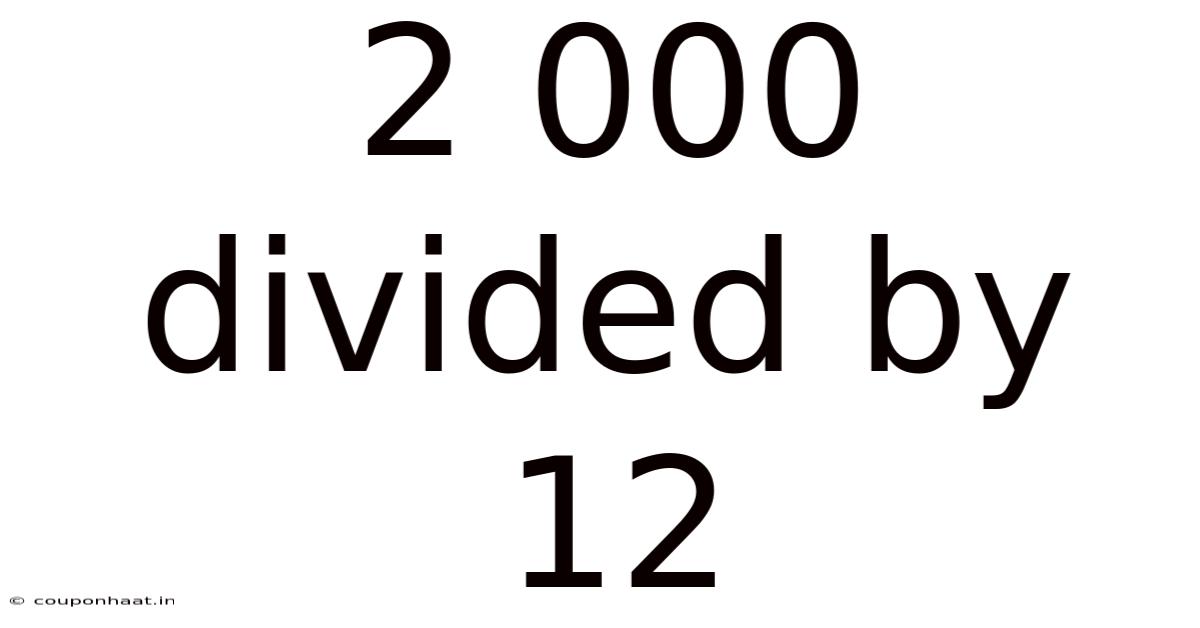
Table of Contents
2,000 Divided by 12: A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
Introduction:
This article explores the seemingly simple calculation of 2,000 divided by 12, delving far beyond the basic arithmetic answer. We’ll unpack the process using various methods, examine the practical applications of such calculations in everyday life, and explore the underlying mathematical concepts. Understanding division isn't just about getting the right answer; it's about grasping the fundamental principles that govern how we quantify and understand the world around us. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to tackle similar problems with confidence and appreciate the broader implications of this seemingly straightforward operation. We will also address common questions and misconceptions surrounding division. Keywords: division, long division, arithmetic, mathematics, fractions, decimals, real-world applications.
Method 1: Long Division
The most traditional and widely understood method for solving 2,000 divided by 12 is long division. This method breaks down the problem into manageable steps, revealing the process clearly.
-
Set up the problem: Write the dividend (2,000) inside the long division bracket and the divisor (12) outside.
12 | 2000 -
Divide the first digit(s): 12 doesn't go into 2, so we consider the first two digits, 20. 12 goes into 20 once (12 x 1 = 12). Write the "1" above the "0" in 2000.
1 12 | 2000 -
Subtract and bring down: Subtract 12 from 20, which leaves 8. Bring down the next digit (0) to make 80.
1 12 | 2000 -12 --- 80 -
Repeat the process: 12 goes into 80 six times (12 x 6 = 72). Write the "6" above the "0" in 2000.
16 12 | 2000 -12 --- 80 -72 -- 8 -
Subtract and bring down: Subtract 72 from 80, leaving 8. Bring down the final digit (0) to make 80.
16 12 | 2000 -12 --- 80 -72 -- 80 -
Final Division: 12 goes into 80 six times (12 x 6 = 72). Write the "6" above the "0" in 2000.
166 12 | 2000 -12 --- 80 -72 -- 80 -72 -- 8 -
Remainder: We have a remainder of 8. This means 2000 divided by 12 is 166 with a remainder of 8. We can express this as a mixed number (166 8/12) or a decimal (approximately 166.67). Simplifying the fraction 8/12 gives us 2/3. Therefore, the final answer is 166 and 2/3.
Method 2: Using Fractions
We can express the division problem as a fraction: 2000/12. Simplifying this fraction provides another way to reach the solution.
-
Find the greatest common divisor (GCD): The GCD of 2000 and 12 is 4.
-
Simplify the fraction: Divide both the numerator and the denominator by the GCD: 2000 ÷ 4 = 500 and 12 ÷ 4 = 3. This simplifies the fraction to 500/3.
-
Convert to a mixed number: Divide 500 by 3: 3 goes into 500 166 times with a remainder of 2. This gives us the mixed number 166 2/3.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
The simplest method is to use a calculator. Enter 2000 ÷ 12 and the calculator will return the answer: 166.666666... This is a repeating decimal, representing the fractional part 2/3.
Real-World Applications
The seemingly simple calculation of 2,000 divided by 12 has numerous real-world applications:
- Finance: Dividing a $2,000 debt equally among 12 months determines a monthly payment of approximately $166.67.
- Measurement: If you have a 2,000-meter-long track and need to divide it into 12 equal segments for training, each segment would be approximately 166.67 meters.
- Inventory Management: If a warehouse contains 2,000 items and they are organized into 12 shelves, each shelf holds roughly 166.67 items.
- Food Distribution: If 2,000 sandwiches need to be distributed evenly to 12 schools, each school receives about 166.67 sandwiches (you'd likely round this up or down depending on the context).
- Project Management: If a project requires 2,000 hours of work and needs to be completed over 12 weeks, each week would need approximately 166.67 hours of work.
These are just a few examples. The principle of dividing a quantity into a number of equal parts is essential in countless fields, from accounting and engineering to culinary arts and logistics.
Understanding Remainders
The remainder of 8 in our long division problem is crucial. It represents the portion of the dividend that couldn't be divided evenly by the divisor. This remainder has practical significance. For example, in the context of distributing sandwiches to schools, the remainder of 8 sandwiches might be distributed randomly or saved for another occasion. The way the remainder is handled depends entirely on the real-world application. Ignoring the remainder may lead to inaccurate results or resource mismanagement.
Decimal Representation vs. Fractions
The decimal representation of 2000/12 (166.666...) is useful for quick approximations and calculations, particularly when using calculators or computers. However, fractions (166 2/3) offer greater precision in scenarios demanding exactness, and avoiding rounding errors. The choice between using a decimal or a fraction depends upon the level of accuracy needed for the specific context.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the exact answer to 2000 divided by 12?
A: The exact answer is 166 2/3. The decimal representation 166.666... is an approximation.
Q: How do I deal with remainders in real-world situations?
A: Remainders require careful consideration based on the context. Sometimes rounding up or down is appropriate. In other situations, the remainder might need to be further divided or allocated differently.
Q: Why are there multiple ways to solve a division problem?
A: Different methods offer various approaches to understanding the underlying concept. Long division demonstrates the step-by-step process, fractions emphasize the relationship between the dividend and divisor, while calculators provide a quick numerical solution. Understanding these different methods provides a deeper understanding of the mathematics.
Q: Is there a simpler way to divide 2000 by 12 without using long division?
A: While long division is the most comprehensive method, you can simplify by initially dividing both numbers by a common factor (like 4, as shown in the fractions method). This reduces the complexity of the calculation.
Q: What if the divisor was a larger number than the dividend?
A: If the divisor is larger than the dividend, the result will be a fraction less than one. For example, 12 divided by 2000 is 0.006.
Conclusion:
Dividing 2,000 by 12, while seemingly a simple calculation, offers a rich opportunity to explore fundamental mathematical concepts and their practical applications. From long division to using fractions and calculators, we've explored various methods. Understanding remainders and the nuances of decimal vs. fractional representations are vital for accurate and contextually appropriate results. The ability to perform this calculation and understand its implications is a cornerstone of numerical literacy and problem-solving skills applicable to countless real-world situations. Mastering these techniques will equip you to confidently tackle similar problems and appreciate the broader mathematical principles at play.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
7 7 10 As A Decimal
Sep 14, 2025
-
Pride And Prejudice Movie Locations
Sep 14, 2025
-
What Is Global Trade Management
Sep 14, 2025
-
Top Line Vs Bottom Line
Sep 14, 2025
-
Summary The Absolutely True Diary
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 000 Divided By 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.